
Imagine this situation: Your reliable computer is no longer as fast as it used to be. While it has many great features, there are times when it runs slowly.
There can be several reasons for your computer’s sluggishness, and one common culprit is insufficient RAM. When your computer doesn’t have enough RAM, it may struggle to handle multiple programs or browser tabs simultaneously.
However, discussing RAM can be challenging if you’re not familiar with the common terminologies. How can you ask questions or talk about the amount of RAM you need without understanding these terms?
1. DIMM/SO-DIMM
You’ll often come across two types of RAM: DIMM and SO-DIMM.
- DIMM: Dual In-Line Memory Module
- SO-DIMM: Small Outline DIMM
Desktop computers (or servers) typically use DIMMs, while laptops, netbooks, and similar devices use the smaller form-factor SO-DIMMs.

It’s important to note that these RAM modules are not interchangeable due to their different sizes. You cannot insert a DIMM into a SO-DIMM slot or vice versa.
2. DDR
DDR stands for Double Data Rate, indicating that two transfers occur during each clock cycle. With each RAM generation, DDR receives an upgrade, resulting in DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5.
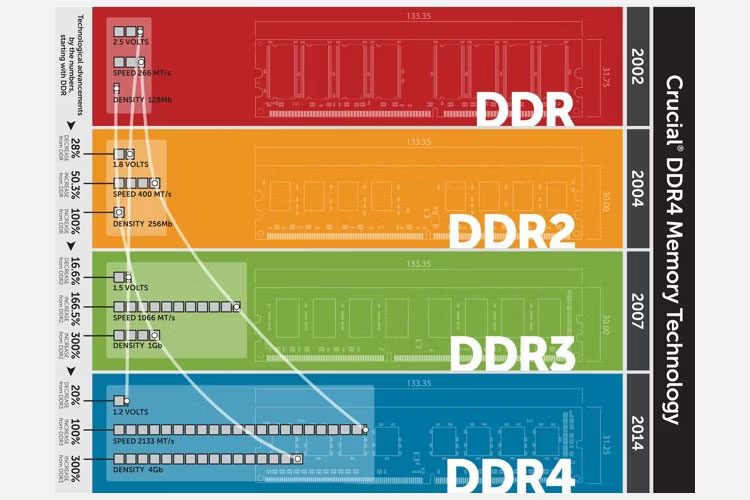
- DDR2: The oldest type of RAM, which is rarely found in modern systems.
- DDR3: Released in 2007, DDR3 RAM is still used in many systems despite being officially replaced by DDR4 in 2014.
- DDR4: Became the dominant standard in 2017, as DDR3’s adoption rate slowed down. In 2021, AMD and Intel CPUs exclusively adopted DDR4 RAM, marking the end of DDR3’s era.
- DDR5: The latest DDR standard, although it is not as widely adopted as DDR4 yet. It offers faster speeds and data transfers compared to its predecessor. AMD’s AM5 platform exclusively supports DDR5, while Intel currently supports both DDR4 and DDR5.
It’s important to mention that different RAM generations cannot be used together.
3. GDDR
You might be thinking we just discussed DDR, but now we’re talking about GDDR. GDDR stands for Graphics Double Data Rate and refers to the memory used in graphics cards.
In simple terms, your computer uses RAM to store data related to the currently running programs and other data that requires quick access.
On the other hand, GDDR RAM is specifically designed for graphics cards to enhance graphical processing speed. It is optimized to provide high bandwidth and optimal graphical performance in conjunction with other GPU components.
GDDR RAM follows a similar naming convention as DDR RAM:
- GDDR6X
- GDDR6
- GDDR5X
- GDDR5
- GDDR4
Generally, higher numbers indicate better performance for GDDR RAM. The latest Nvidia GPUs utilize GDDR6X for maximum performance, while AMD continues to use GDDR6.
4. Capacity & Transfer Speed
When browsing through RAM options at an online or physical computer store, you’ll come across various numbers. While they may appear overwhelming, there are only a few important ones to focus on.
Firstly, consider the capacity, which refers to how much data your RAM can hold. This is typically indicated by values like 4GB, 8GB, or 16GB. Although other RAM sizes are available, a minimum of 8GB RAM is recommended for a modern PC.
While higher capacity is generally preferable, there’s no need to overspend if you won’t fully utilize the extra space. For example, if your computer usage primarily involves web browsing, email checking, video watching, and document writing,
8GB RAM will suffice. However, more demanding tasks require greater capacity.
The next aspect to consider is the transfer speed, measured in megatransfers per second (MT/s). For instance, you may encounter RAM labeled as DDR4-3200, indicating an operating speed of 3,200 MT/s. Faster RAM options are available but come at a higher cost.
For most people, capacity is more important than transfer speed in the majority of cases. Having 16GB of DDR4-1600 RAM will provide more benefits than having 8GB of DDR4-2400 RAM.
5. RAM Latency (CAS) and Timings
Capacity and data transfer rates aren’t the only factors that matter in RAM specifications. You might also notice a series of numbers like CL 16-18-18-36.
“CL” represents the RAM CAS latency, where CAS stands for Column Address Strobe. While these terms don’t require extensive understanding, it’s worth knowing that a lower CAS value typically indicates faster data access by your RAM.
You may come across RAM options with matching data transfer rates, such as DDR-3200, but with different CAS timings. For example, one set may have a CL18 rating, while another may have CL16. In this case, the CL16 RAM will perform tasks slightly faster, but it will be more expensive.
6. PC3, PC4, & PC5 RAM
PC3, PC4, and PC5 correspond to DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5, respectively. However, they measure RAM performance using a slightly different approach.
While DDR4-xxxx indicates the per-bit data rate, PC4-xxxxx reflects the overall data rate of your RAM in MB/s. You can calculate the total data rate of a RAM module by multiplying its frequency by eight.
For example, if you encounter DDR4-3200 RAM, multiplying that figure by eight will give you the total data rate, such as 25,600 MB/s, in the case of PC4-25600.
7. RAM Slots
Before purchasing RAM, it’s essential to check how many RAM slots your motherboard has. The number of slots will determine the number of RAM modules you can install.
If your motherboard has two RAM slots, you can buy a pair of matching modules. RAM kits often include two or four modules (in the case of four slots). While it’s not mandatory to match your RAM modules, they tend to perform best when they have the same capacity and use the same voltages.
Additionally, if you use RAM modules with different frequencies or speeds, the rest of your RAM will adjust to the lower frequency to maintain system stability.
8. ECC Memory
ECC (Error-correcting code) memory is a special type of computer data storage that can identify and correct most common forms of data corruption.
ECC memory chips are primarily used in computers that require error-free operation, such as financial or scientific computing systems or file servers. Usually, systems equipped with ECC memory experience fewer crashes due to single-bit errors compared to systems without ECC memory.
However, gaming with ECC memory is not recommended as studies show that ECC RAM tends to perform slower than standard RAM, according to Puget Systems.
The inclusion of ECC RAM in this list is to ensure that you don’t accidentally purchase it.
Buy RAM with Confidence
Purchasing RAM doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Armed with a few essential pieces of knowledge about RAM jargon, you’ll be able to make informed decisions when buying RAM, upgrading your system, and more.
Although some RAM terms may initially seem confusing, once you become familiar with them, everything falls into place.



