
Running Android OS on a PC opens up a world of possibilities, merging the convenience of a computer with the versatility of Android applications. Whether you’re looking to enjoy mobile gaming, productivity apps, or a familiar mobile interface, the best Android OS for PC can transform your experience. In this article, we will explore and evaluate the 12 best Android OS options for both 64-bit and 32-bit systems. From well-known names like Bluestacks and Phoenix OS to niche offerings like FydeOS and Anbox OS, we will delve into the features, pros, and cons of each, helping you find the perfect Android OS to suit your PC needs. So let’s dive in and discover the exciting world of Android on PC.
1. Bluestacks
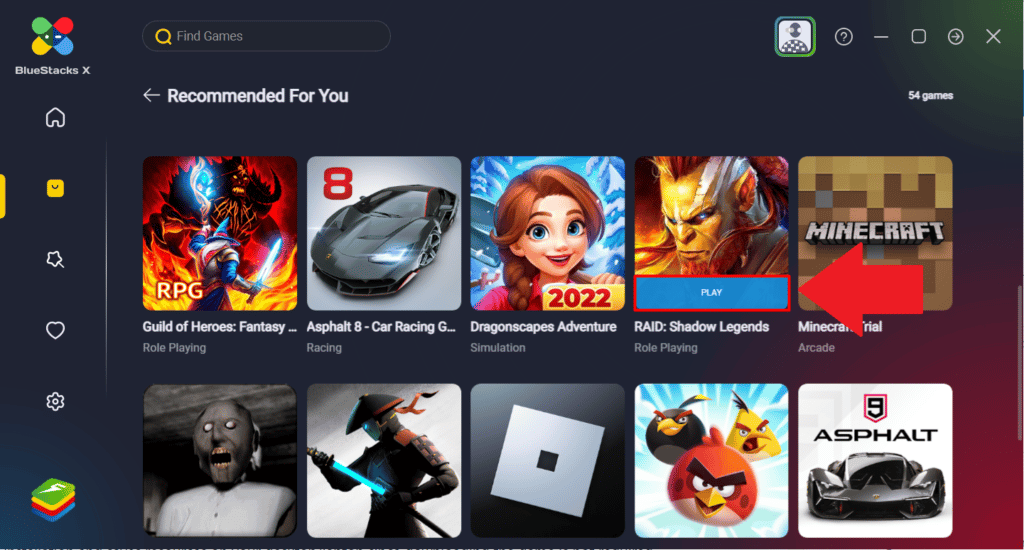
Bluestacks is a popular Android emulator that allows you to run Android apps and games on your PC. With a user-friendly interface and seamless performance, Bluestacks bridges the gap between mobile and desktop environments. It emulates the Android ecosystem, providing access to the Google Play Store and enabling you to enjoy a wide range of apps and games on a larger screen.
Pros:
- Versatile App Compatibility: Bluestacks supports a vast library of Android apps and games, giving you access to popular titles and niche applications.
- Intuitive Interface: The user-friendly interface of Bluestacks makes it easy for both beginners and experienced users to navigate and utilize its features.
- Multi-Instance Functionality: Bluestacks allows you to run multiple instances simultaneously, enabling you to multitask and use different apps simultaneously.
- Gaming Features: With Bluestacks, you can enjoy advanced gaming features like key mapping, macros, and gamepad support, enhancing your gaming experience on PC.
- Regular Updates: Bluestacks regularly releases updates, ensuring compatibility with the latest Android versions and improving performance and stability.
Cons:
- High System Requirements: Bluestacks may require a powerful PC configuration to run smoothly, especially for resource-intensive games and apps.
- Limited Customization: The level of customization options in Bluestacks is relatively limited compared to some other Android OS options for PC.
- Occasional Performance Issues: While Bluestacks generally offers smooth performance, some users may experience occasional lag or performance hiccups depending on their PC specifications.
- Advertisements: Bluestacks displays advertisements within the emulator, which can be disruptive for some users. However, an ad-free version is available through a subscription.
2. PrimeOS
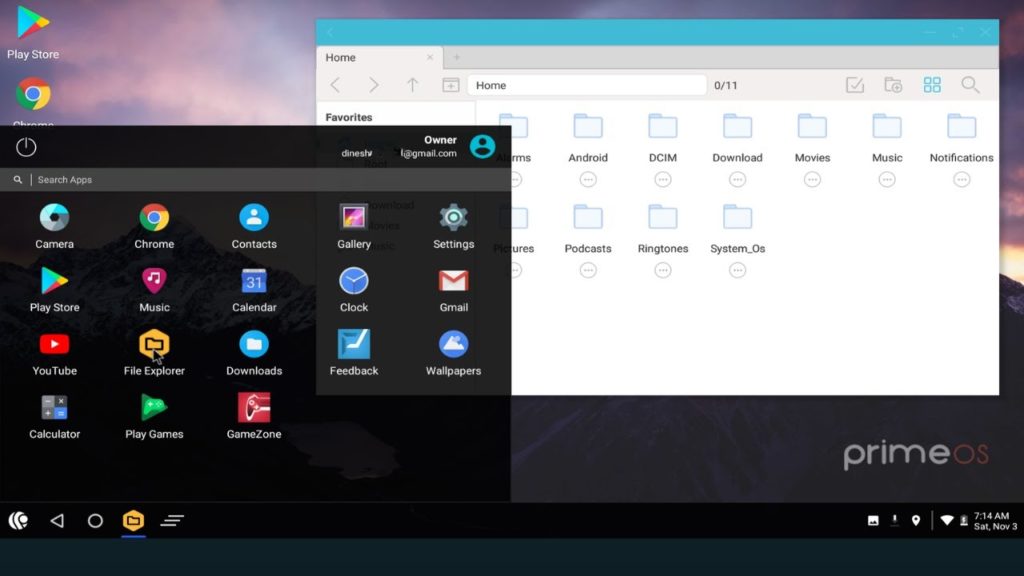
PrimeOS is a full-fledged Android operating system designed specifically for PCs, providing a desktop-like experience with Android functionality. It aims to bridge the gap between mobile and desktop computing, offering a familiar interface for users transitioning from traditional desktop environments to Android.
Pros:
- Desktop-like Experience: PrimeOS provides a desktop-like interface with a taskbar, start menu, and resizable windows, giving users a familiar and productive computing experience.
- Gaming Performance: PrimeOS is optimized for gaming, offering smooth gameplay and support for keyboard and mouse controls. It also includes features like key mapping and macro support.
- Multitasking Capabilities: With its multi-window support, PrimeOS allows users to run multiple apps simultaneously, enhancing productivity and convenience.
- File Manager: PrimeOS includes a built-in file manager, enabling easy access and management of files and folders on your PC.
- Compatibility: PrimeOS is compatible with both 64-bit and 32-bit systems, providing flexibility for a wide range of PC configurations.
Cons:
- Limited App Compatibility: While PrimeOS supports a significant number of Android apps, there may still be some compatibility issues with certain apps and games.
- Learning Curve: For users unfamiliar with Android or those accustomed to traditional desktop environments, there may be a learning curve in navigating PrimeOS’s interface and features.
- System Requirements: PrimeOS may require a relatively powerful PC configuration to run smoothly, especially when running resource-intensive apps or games.
- Limited Customization: Compared to some other Android OS options, PrimeOS offers limited customization options for personalizing the desktop environment.
3. Phoenix OS

Phoenix OS is an Android-based operating system designed to bring the Android experience to PCs. It offers a desktop-like interface with enhanced productivity features, making it an appealing choice for users looking to use Android on their personal computers.
Pros:
- Desktop Interface: Phoenix OS provides a familiar desktop interface, complete with a taskbar, start menu, and resizable windows, allowing users to navigate and multitask seamlessly.
- Gaming Performance: With its gaming optimizations, Phoenix OS delivers smooth gaming performance and supports keyboard and mouse controls, making it ideal for gaming enthusiasts.
- Productivity Features: Phoenix OS offers features like multiple windows, file manager, and a taskbar with system tray, enabling users to enhance their productivity and efficiently manage tasks.
- Customization Options: Users can personalize the Phoenix OS desktop with different themes, wallpapers, and icon packs, allowing for a tailored experience.
- Compatibility: Phoenix OS is compatible with both 64-bit and 32-bit systems, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of PC configurations.
Cons:
- Limited App Support: Although Phoenix OS supports many Android apps, there may still be compatibility issues with certain apps or games due to differences in hardware and software configurations.
- System Requirements: Phoenix OS may require a relatively powerful PC configuration for optimal performance, especially when running resource-intensive applications.
- Updates and Support: Some users have reported limited updates and support from the developers, which may impact the availability of bug fixes and new features.
4. Chrome OS
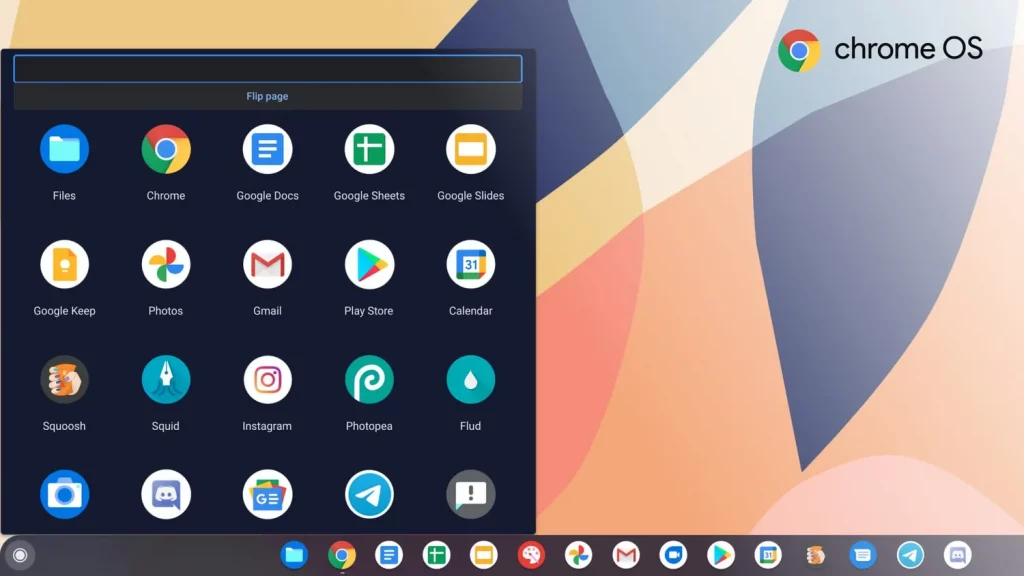
Chrome OS is a lightweight and fast operating system developed by Google, primarily designed for Chromebooks. It offers a streamlined and secure computing experience, emphasizing web-based applications and cloud storage integration.
Pros:
- Speed and Performance: Chrome OS is known for its fast boot times and overall responsiveness, making it an efficient choice for users seeking a quick and hassle-free computing experience.
- Security: Chrome OS is built with security in mind, with automatic system updates, sandboxed applications, and verified boot, reducing the risk of malware and protecting user data.
- Web-Centric Approach: As a web-centric operating system, Chrome OS seamlessly integrates with Google’s suite of web-based applications, such as Google Docs, Gmail, and Google Drive, enabling easy access and collaboration on documents and files.
- Simple and User-Friendly Interface: The interface of Chrome OS is clean and intuitive, designed for simplicity and ease of use, making it ideal for beginners and users who prefer a straightforward computing experience.
- Offline Capabilities: While Chrome OS emphasizes web-based applications, it also offers offline capabilities for certain apps, allowing users to work or enjoy entertainment even without an internet connection.
Cons:
- Limited Application Support: Chrome OS primarily relies on web-based applications, which may limit access to certain software or programs that are only available as native desktop applications.
- Dependency on Internet Connection: Chrome OS heavily relies on an internet connection for full functionality, and certain features may be limited or unavailable without an active internet connection.
- Hardware Compatibility: Chrome OS is designed to run on specific hardware configurations, mainly Chromebooks, limiting its availability for installation on non-supported devices.
- Gaming Limitations: Chrome OS is not known for its gaming capabilities, as it has limited support for resource-intensive games and lacks compatibility with popular gaming platforms.
5. Android x86
Android x86 is an open-source project that aims to port the Android operating system to the x86 architecture, allowing it to run on traditional PCs and laptops. It provides a native Android experience on non-mobile devices, offering access to the vast ecosystem of Android apps and services.
Pros:
- Compatibility: Android x86 supports a wide range of hardware configurations, making it compatible with many PCs and laptops, including older devices that may not support other Android OS options.
- Native Android Experience: With Android x86, users can enjoy a true Android experience on their PCs, complete with the familiar interface, app compatibility, and Google Play Store access.
- Customization and Flexibility: Android x86 provides a high level of customization, allowing users to modify system settings, install custom ROMs, and experiment with different Android configurations.
- Regular Updates and Community Support: The Android x86 project is actively maintained by a community of developers, ensuring regular updates, bug fixes, and new features to enhance the user experience.
Cons:
- Potential Compatibility Issues: While Android x86 supports a wide range of hardware, there may still be compatibility issues with certain PC configurations, resulting in driver or functionality limitations.
- Technical Expertise Required: Setting up and installing Android x86 on a PC may require some technical knowledge, as it involves partitioning drives, configuring boot options, and dealing with potential installation issues.
- App Optimization: Some Android apps may not be optimized for the x86 architecture, leading to performance issues or incompatibilities.
- Limited Support for Touchscreens and Sensors: Android x86 may have limited support for touchscreen displays and certain sensors commonly found in mobile devices, impacting the usability and functionality on touch-enabled PCs.
6. Remix OS

Remix OS is an Android-based operating system designed to provide a desktop-like experience on PCs and laptops. It offers a customizable and productive interface, enabling users to seamlessly switch between Android apps and traditional desktop applications.
Pros:
- Desktop Interface: Remix OS features a user-friendly desktop interface that resembles a traditional operating system, with a taskbar, start menu, and resizable windows, enhancing productivity and ease of use.
- Multitasking Capabilities: Users can run multiple Android apps in separate windows, enabling efficient multitasking and enhancing productivity on a larger screen.
- Compatibility with Android Apps: Remix OS supports a wide range of Android apps, giving users access to the vast Android ecosystem and the ability to utilize their favorite mobile apps on a PC.
- File Manager and Productivity Tools: Remix OS includes a built-in file manager, as well as productivity tools like a text editor and a calculator, providing essential functionalities for work and everyday tasks.
- Fast and Responsive: Remix OS offers fast boot times and responsive performance, allowing users to navigate through the interface and run applications smoothly.
Cons:
- Limited Updates and Development: Remix OS has faced limited updates and development in recent years, which may result in compatibility issues with newer hardware or apps.
- Hardware Compatibility: While Remix OS supports a range of PC hardware, certain configurations may have compatibility issues, leading to driver or functionality limitations.
- App Optimization: Some Android apps may not be fully optimized for Remix OS, resulting in occasional performance issues or compatibility limitations.
- Learning Curve: Users who are unfamiliar with Android or transitioning from a traditional desktop environment may experience a learning curve in adapting to the Android-based interface and its unique features.
7. Bliss OS x86
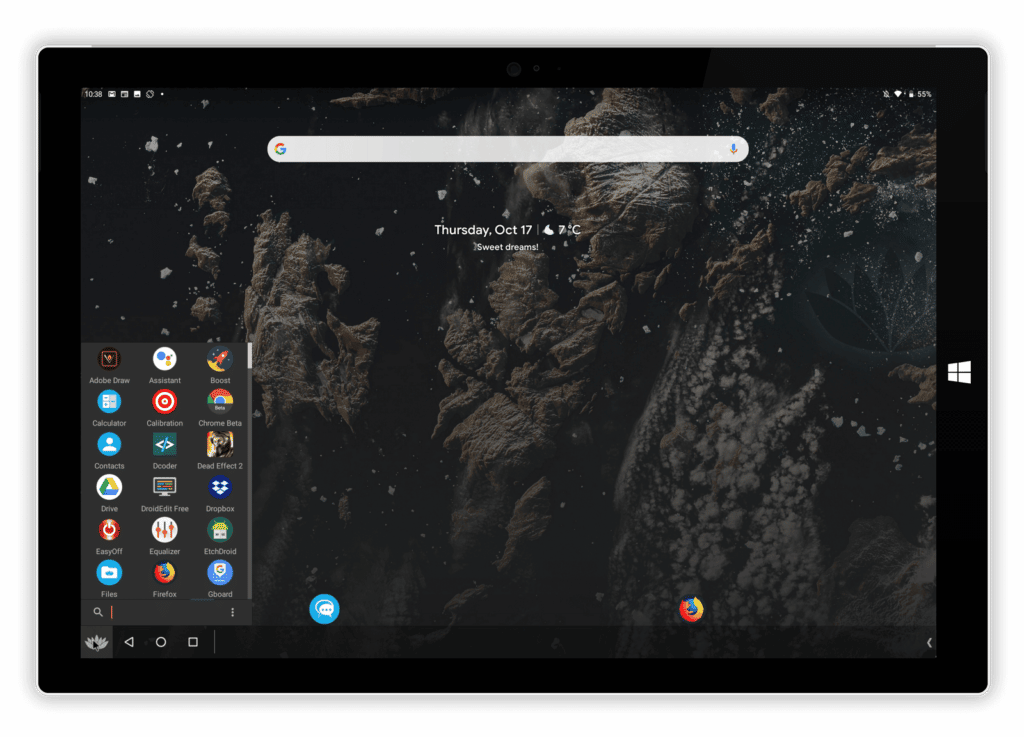
Bliss OS x86 is an open-source operating system based on Android, specifically designed for x86-based PCs and laptops. It offers a unique and customizable Android experience, allowing users to harness the power of Android on their non-mobile devices.
Pros:
- Android Customization: Bliss OS x86 provides a high level of customization, allowing users to personalize their Android experience with various themes, icons, and wallpapers.
- Multiwindow Support: Users can take advantage of the multiwindow feature, enabling them to run multiple Android apps simultaneously and enhance productivity on a larger screen.
- Android App Compatibility: Bliss OS x86 supports a wide range of Android apps, giving users access to a vast library of applications and services available on the Google Play Store.
- Regular Updates and Community Support: Bliss OS x86 is actively maintained by a community of developers, ensuring regular updates, bug fixes, and new features to enhance the user experience.
- Performance Optimization: Bliss OS x86 is optimized for x86-based hardware, delivering smooth performance and efficient resource utilization on PCs and laptops.
Cons:
- Learning Curve: Users who are not familiar with Android or transitioning from a traditional desktop environment may experience a learning curve in adapting to the Android-based interface and its unique features.
- App Optimization: While Bliss OS x86 supports a wide range of Android apps, some apps may not be fully optimized for the x86 architecture, leading to occasional performance issues or compatibility limitations.
- Hardware Compatibility: While Bliss OS x86 supports many PC configurations, there may still be compatibility issues with certain hardware components, resulting in driver or functionality limitations.
- Limited Support: As an open-source project, Bliss OS x86 may have limited official support channels, which can affect the availability of technical assistance and updates.
8. Openthos
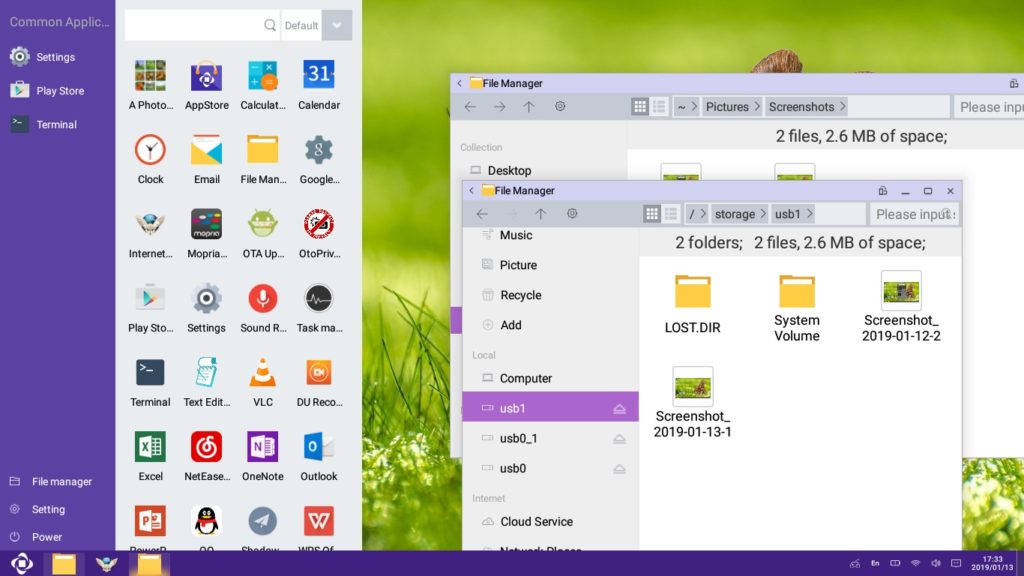
Openthos is an open-source operating system that combines the Android platform with the functionality of a traditional desktop OS. It aims to provide users with a versatile and familiar computing experience, offering Android apps alongside desktop applications on PCs and laptops.
Pros:
- Dual Functionality: Openthos allows users to switch seamlessly between Android apps and traditional desktop applications, providing a hybrid experience that caters to different computing needs.
- Android App Compatibility: Users can access a vast array of Android apps through the Google Play Store, enabling them to enjoy popular mobile applications on a larger screen.
- Desktop Features: Openthos incorporates several desktop features, including a taskbar, file manager, and multiwindow support, enhancing productivity and ease of use.
- Customization Options: Users can customize the appearance and behavior of Openthos, such as modifying themes, wallpapers, and desktop layouts, to suit their preferences.
- Open-Source and Community-Driven: Openthos is an open-source project, allowing developers and users to contribute to its development and improvement, ensuring regular updates and bug fixes.
Cons:
- Learning Curve: Users who are not familiar with Android or transitioning from a traditional desktop environment may need time to adapt to Openthos’ combined Android and desktop interface.
- App Optimization: Some Android apps may not be fully optimized for the desktop environment, resulting in occasional performance issues or compatibility limitations.
- Hardware Compatibility: While Openthos supports a range of PC configurations, there may be compatibility issues with specific hardware components, impacting functionality or driver support.
- Limited Application Support: Openthos may not have the same breadth of desktop applications available as other traditional desktop operating systems, which can limit software choices for certain users.
9. Genymotion
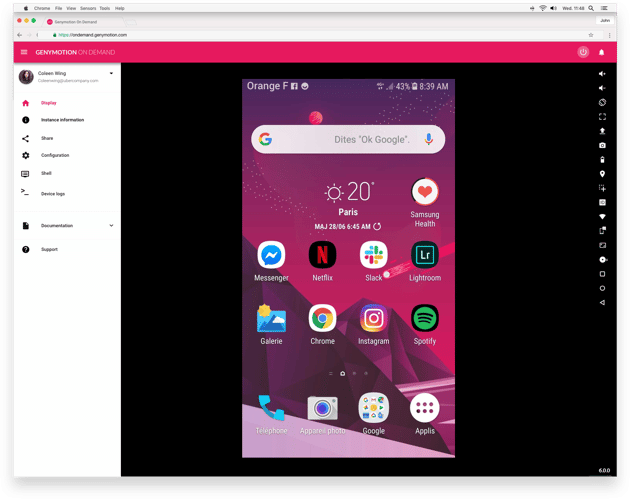
Genymotion is a powerful Android emulator primarily used by developers for testing and running Android applications. It provides a virtual Android environment on a PC or laptop, allowing developers to simulate various device configurations and test their apps across different Android versions.
Pros:
- Wide Range of Virtual Devices: Genymotion offers a vast selection of pre-configured virtual devices with different Android versions, screen resolutions, and hardware characteristics, allowing developers to test their apps on various device configurations.
- Fast and Efficient Performance: Genymotion is known for its fast and efficient performance, providing smooth emulation of Android devices and ensuring a seamless testing experience for developers.
- Advanced Features and Tools: Genymotion provides a range of advanced features and tools that aid developers in app testing, such as GPS simulation, network latency emulation, and sensor simulation.
- Integration with Development Tools: Genymotion seamlessly integrates with popular development tools like Android Studio and Eclipse, making it easy for developers to test their apps without switching between different environments.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Genymotion is compatible with Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems, allowing developers to test their apps across multiple platforms.
Cons:
- Limited Features for Non-Developers: Genymotion is primarily designed for developers, so non-technical users may find its interface and features overwhelming or unnecessary.
- Paid Licenses for Advanced Features: While Genymotion offers a free version with basic features, some advanced functionalities and virtual devices require a paid license, which may not be suitable for all developers.
- Resource Intensive: Running Genymotion and multiple virtual devices simultaneously can be resource-intensive, requiring a powerful computer with sufficient RAM and CPU capabilities.
- Learning Curve: Non-technical users or those new to Android development may face a learning curve when setting up and using Genymotion for the first time.
10. FydeOS
FydeOS is a cloud-based operating system that brings the power of Chrome OS to non-Chromebook devices. It offers a secure and streamlined computing experience, with a focus on web-based applications and cloud storage integration.
Pros:
- Chrome OS Features: FydeOS inherits many features from Chrome OS, including a simple and user-friendly interface, fast boot times, and seamless integration with Google services like Google Drive and Chrome Web Store.
- Web-Centric Experience: FydeOS emphasizes web-based applications, allowing users to access popular web services, productivity tools, and entertainment platforms directly from the browser, reducing the need for local installations.
- Security and Updates: FydeOS benefits from Chrome OS’s robust security architecture, providing built-in protection against malware and automatic system updates to ensure users have the latest security patches.
- Chrome Extension Compatibility: FydeOS supports Chrome extensions, allowing users to enhance their browsing experience with a wide range of tools and add-ons available from the Chrome Web Store.
- Versatile Device Support: FydeOS is designed to run on various non-Chromebook devices, including PCs, laptops, and single-board computers, providing users with the flexibility to choose their hardware.
Cons:
- Limited Offline Functionality: As a cloud-based operating system, FydeOS relies heavily on internet connectivity, and some features may be limited or unavailable when offline.
- Dependency on Google Services: FydeOS heavily integrates with Google services, which may be a drawback for users who prefer alternative cloud storage providers or have privacy concerns.
- Application Availability: While FydeOS supports a wide range of web applications, some software and specialized applications may not be available or optimized for the Chrome OS ecosystem.
- Learning Curve for Non-Chrome OS Users: Users unfamiliar with Chrome OS may require some time to adapt to the operating system’s interface and unique workflow.
11. Anbox OS
Anbox OS is a unique Android-based operating system that allows users to run Android applications natively on their Linux distributions. It utilizes containerization technology to create a bridge between the Android ecosystem and the Linux operating system.
Pros:
- Seamless Integration: Anbox OS seamlessly integrates Android applications into the Linux environment, enabling users to run their favorite Android apps without the need for an emulator or virtual machine.
- Native Performance: Unlike traditional Android emulators, Anbox OS leverages containerization to provide near-native performance for running Android applications, resulting in smoother and more responsive user experiences.
- Access to Android App Ecosystem: With Anbox OS, users have access to the vast Android app ecosystem, including popular social media apps, productivity tools, games, and more, all within their Linux environment.
- Easy Installation and Setup: Anbox OS simplifies the installation and setup process, making it accessible for both advanced Linux users and beginners who are new to the platform.
- Customization and Compatibility: Anbox OS supports customization options, allowing users to tailor the system to their preferences, and it is compatible with a wide range of Linux distributions.
Cons:
- Limited Device Support: Anbox OS is currently available only for Linux distributions, which may restrict its usage for users on other operating systems.
- Dependency on Linux Compatibility: The compatibility and functionality of Anbox OS can vary depending on the specific Linux distribution being used, requiring users to ensure that their distribution supports Anbox OS.
- Performance Variability: While Anbox OS aims to provide near-native performance, certain resource-intensive applications or games may experience performance limitations or compatibility issues.
- Limited Hardware Integration: Anbox OS focuses on application compatibility and performance rather than full hardware integration, so features like camera access or device-specific sensors may not be fully supported.
12. LineageOS
LineageOS is a popular open-source operating system based on the Android platform. It offers a clean and customizable user interface, giving users the freedom to personalize their device while providing a stable and secure mobile experience.
Pros:
- Open-Source Nature: LineageOS is built on the principles of open-source software, promoting transparency, community collaboration, and user empowerment. This allows for continuous development, bug fixes, and security updates from a dedicated community of developers.
- Customization Options: LineageOS provides extensive customization options, allowing users to tailor their device’s appearance, features, and behavior according to their preferences. This includes the ability to install custom themes, modify system settings, and use third-party apps to enhance the user experience.
- Enhanced Privacy and Security: LineageOS prioritizes user privacy and security by implementing features such as Privacy Guard, which gives users granular control over app permissions, and the ability to install security patches promptly.
- Performance and Stability: LineageOS is known for its optimized performance and stability, delivering a smooth and responsive user experience even on older or less powerful devices. It focuses on efficiency and resource management to maximize device performance.
- Wide Device Support: LineageOS supports a wide range of Android devices, including smartphones and tablets from various manufacturers, ensuring that users have the flexibility to choose the hardware that suits their needs.
Cons:
- Technical Knowledge Required: Customizing and installing LineageOS may require some technical knowledge and familiarity with the Android platform, making it less accessible for users with limited technical expertise.
- Limited Official Device Support: While LineageOS supports a wide range of devices, official support may vary, and users of less popular or newer devices may have to rely on unofficial builds or community-supported versions.
- Risk of Voiding Warranty: Installing LineageOS or any custom ROM on a device may void the manufacturer’s warranty, and users should proceed with caution and understand the potential risks involved.
- App Compatibility: Some apps may not be fully compatible with LineageOS due to its customizations or lack of Google Play Services. While there are alternative app stores and methods to access apps, compatibility can vary.
Conclusion
Overall, the Android OS options for PC listed in this article showcase the versatility and adaptability of the Android platform, enabling users to enjoy the benefits of Android apps and functionalities on their PCs. Whether it’s for productivity, gaming, or personalization, these Android OS choices offer diverse solutions for users seeking an enhanced Android experience on their PCs.



